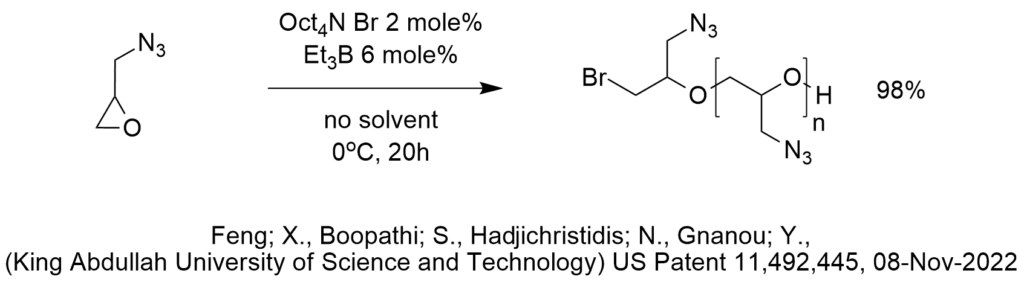
Glycidyl azide polymer (GAP) is a high energy material used in propellants. It can be formed by displacement of the chloride by azide in polyepichlorohydrin (PECH) using PTC. In this patent, GAP is formed safely under mild reaction conditions by the polymerization of glycidyl azide using a halide initiator in the presence of the Lewis acid triethyl borane. Polymerization of glycidyl azide assures 100% azide content since it does not depend on complete displacement of all of the chloride of PECH.
Quat salts are used to supply halides as initiators for anionic ring opening polymerization (AROP).
While this reaction is NOT phase-transfer catalysis, it leverages two characteristics useful in PTC systems which are [1] the ability of a quaternary ammonium cation to solubilize halides in an organic reaction phase and [2] activate the nucleophilicity of the halide by forming a loose ion pair between the quat cation and the halide.
In the reaction shown in the diagram, the larger ionic radius of tetraoctyl ammonium relative to tetrabutyl ammonium results in higher conversion under comparable reaction conditions.
This reaction must avoid displacement of the azide by bromide or chloride since that is a known PTC reaction. This might be one reason that the polymerization is performed at a temperature of 0 C (sometimes at -10 C).
Triethyl borane is used as a Lewis acid to enhance the reaction, possibly by associating with the oxygen atom of the epoxide to assist the ring opening at the lower temperature.
When the polymerization was performed in the presence of carbon dioxide, a polycarbonate copolymer was formed. That polymerization was performed at 25 C. In this case, tetrabutyl ammonium azide was used as the quat salt initiator. The inventors did not specify why the quat azide was preferentially used for the glycidyl azide polycarbonate while they preferentially used quat bromide for GAP without carbon dioxide. We might speculate that at the “higher temperature” of 25 C, the presence of halides might displace azide of the glycidyl azide or the azide on the polymer.